Introduction

The conflict between Ukraine and Russia, which began in earnest in 2014 with the annexation of Crimea, has evolved into a complex and multifaceted geopolitical crisis. This prolonged conflict has significant implications for global politics, security, and humanitarian conditions. Understanding the reality of this conflict requires a comprehensive examination of its origins, ongoing developments, and potential future trajectories.

Historical Context and Causes
Soviet Legacy
The roots of the Ukraine-Russia conflict can be traced back to the Soviet era. Ukraine was one of the founding republics of the Soviet Union, and its relationship with Russia was marked by both cooperation and contention. The dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991 led to Ukraine’s independence, but it left behind a complex legacy of political, economic, and cultural ties with Russia.

Crimea and Eastern Ukraine
The immediate causes of the conflict can be linked to the political upheaval in Ukraine in early 2014. The Euromaidan protests, which began in November 2013, were driven by widespread dissatisfaction with then-President Viktor Yanukovych’s decision to suspend an association agreement with the European Union in favor of closer ties with Russia. These protests, which culminated in Yanukovych’s ousting in February 2014, were perceived by Russia as a Western-backed coup, undermining its influence in the region.
In March 2014, Russia responded by annexing Crimea, a move widely condemned by the international community as a violation of international law. The annexation was followed by unrest in Eastern Ukraine, where pro-Russian separatists declared independence in the Donetsk and Luhansk regions, leading to a violent and ongoing conflict.

Ethnic and Cultural Tensions
Ethnic and cultural tensions have also played a role in the conflict. In Crimea and Eastern Ukraine, significant Russian-speaking populations have historically leaned towards closer ties with Russia. These regional differences have been exacerbated by political manipulations and media portrayals, fueling separatist sentiments and complicating peace efforts.
Key Phases of the Conflict
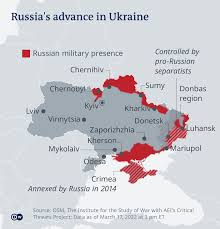
Initial Conflict and Annexation
The initial phase of the conflict was marked by Russia’s annexation of Crimea in early 2014, which was followed by the outbreak of violence in Eastern Ukraine. The Ukrainian government, backed by Western nations, accused Russia of direct involvement in the conflict through military support for separatists.
Minsk Agreements
In an attempt to de-escalate the conflict, the Minsk Agreements were brokered by the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) in September 2014 and February 2015. These agreements aimed to establish a ceasefire and provide a framework for political resolution, including a degree of autonomy for the Donetsk and Luhansk regions. However, implementation has been problematic, with frequent violations of the ceasefire and continued fighting.

Escalation and Full-Scale Invasion
The conflict saw a dramatic escalation in February 2022 when Russia launched a full-scale invasion of Ukraine. This marked a significant shift from the localized conflict in Eastern Ukraine to a broader, high-intensity war. The invasion led to widespread international condemnation, severe sanctions against Russia, and increased military and economic support for Ukraine from Western nations.
Current Situation
Military Developments
As of August 2024, the conflict remains active, with ongoing military engagements across Ukraine. Key areas of contention include the Donbas region, where fighting continues between Ukrainian forces and Russian-backed separatists. The full-scale invasion has resulted in significant casualties on both sides and widespread destruction in affected areas.

Russian forces have faced challenges in achieving their objectives, leading to a protracted and costly war. Ukrainian resistance has been bolstered by Western military aid, including advanced weaponry and training. The conflict has also seen increased involvement of private military contractors and irregular forces.
Humanitarian Impact
The humanitarian impact of the conflict has been severe. Millions of people have been displaced, both within Ukraine and across international borders. The conflict has led to a significant humanitarian crisis, with shortages of food, medicine, and other essential supplies in conflict zones.
International organizations, including the United Nations and various non-governmental organizations, have been working to provide aid and support to affected populations. However, access to these areas remains challenging due to ongoing hostilities and logistical issues.
Economic Consequences
The economic consequences of the conflict are far-reaching. For Ukraine, the war has caused substantial damage to infrastructure and disruption of economic activities. The economy has contracted, and the cost of rebuilding and recovery will be immense.

Russia, too, has faced significant economic repercussions due to international sanctions. These sanctions have targeted various sectors, including finance, energy, and defense, contributing to economic isolation and impacting Russia’s economic stability.
Diplomatic Efforts and Peace Prospects
International Diplomacy
International diplomacy continues to play a critical role in seeking a resolution to the conflict. Various countries and international organizations have been involved in mediating peace talks and negotiating potential settlements. The United Nations and the European Union have been active in addressing the humanitarian aspects and pushing for a diplomatic resolution.

Challenges to Peace
Several factors complicate the path to peace. Deep-seated mistrust between the parties, divergent interests, and unresolved issues from previous agreements pose significant challenges. The status of Crimea and the future governance of the Donbas region remain contentious issues that require careful negotiation.
The involvement of external actors, including the United States and European countries, has also added layers of complexity. While these nations support Ukraine and impose sanctions on Russia, they also have to balance their strategic interests and avoid escalation into a broader conflict.
Future Prospects

The future of the conflict remains uncertain. Several scenarios are possible, including continued stalemate, a negotiated settlement, or further escalation. The resolution of the conflict will depend on various factors, including:
- Negotiations and Compromises: Both sides will need to make significant concessions to reach a lasting agreement. This may involve compromises on territorial issues, political autonomy, and security guarantees.
- International Pressure: Continued international pressure, both diplomatic and economic, may influence the parties to seek a resolution. Sanctions and diplomatic isolation may play a role in pushing Russia towards negotiations.
- Domestic Dynamics: Internal political dynamics in both Russia and Ukraine will impact the conflict. Public opinion, political stability, and leadership changes may influence the direction of the conflict.
- Humanitarian Considerations: The ongoing humanitarian crisis will continue to be a driving force behind international efforts to resolve the conflict. Addressing the needs of affected populations and rebuilding war-torn areas will be critical to any peace process.


